
Solar Cycle 25
How ionospheric disturbances may impact GNSS-based positioning
Solar flares and disturbances are on the rise and expected to peak in 2025, as part of Solar Cycle 25. These flares and disturbances may impact satellites circling the Earth. As such, you may experience interruptions in receiving GNSS signals, impacting the function of your GNSS receiver and GNSS-based positioning services which can lead to a decrease in the precision of your position during the anticipated event. The severity of an interruption will depend on the type of positioning service, device and your geographic location. We anticipate interruptions may be widespread geographically, and may last up to several hours in some cases.
Ionosphere Total Electron Content (TEC) info
To access the map showing the current TEC as observed and modeled by the Trimble® global reference station network, visit the Trimble Positioning Hub
Note: Click the Layers icon in the upper-right corner of the screen to display TEC and Scintillation. Map data is updated every 10 minutes.
Ionosphere scintillation info
To access the map showing the current scintillation events as observed and modeled by Trimble’s global reference station network, visit the Trimble Positioning Hub. Avoiding scintillation, or taking multiple observations of a point during different periods of the day and different ionospheric conditions, can increase reliability.
Note: Click the Layers icon in the upper-right corner of the screen to display TEC and Scintillation. Map data is updated every 10 minutes.
Frequently asked questions
Solar Cycle 25 is the name given to the current cycle of ionospheric disturbances, caused by the Sun’s regular flare activity, that are expected to peak over the next 3 years, through 2025. This is a natural phenomenon with unpredictable levels of intensity that occurs approximately every 11 years.
Any technology leveraging high-frequency radio signals may be impacted by this. This includes GNSS signals used for positioning, navigation and in GNSS correction services.
During periods of higher solar activity, like Solar Cycle 25, disturbances to the ionosphere can result in scintillation events. During a scintillation event, your reference station may lose tracking lock and encounter cycle slips. These cycle slips can degrade your positioning performance by precluding some satellites being included in your base/rover correction stream, and result in decreased precision at the rover.
The signals from the GNSS satellites are disrupted as they pass through the atmosphere. Each day, as portions of the Earth's atmosphere are excited by the Sun, the Total Electron Content (TEC) increases. Multi-frequency GNSS receivers can help mitigate the impact of TEC, but during periods of higher solar activity, like Solar Cycle 25, the highest electron densities may result in decreased precision.
At Trimble, making our customers’ work better is our top priority. Our goal is to ensure customers are informed of Solar Cycle 25 and can plan for possible disruptions caused by increased solar activity.
During peaks of solar activity, where certain portions of the ionosphere are excited, higher TEC values (and therefore greater signal delays) will occur. Space weather, such as sunspots, can disturb the upper ionosphere, causing small-scale irregularities which can lead to scintillation.
While TEC and scintillation may typically occur at key times throughout the day, such as midday or dusk, that is not always the case. We suggest users utilize multi-frequency and multi-constellation receivers and plan ahead by using our GNSS Planning Online tool and avoid working during times where there is high probability of interference.
Solar flares are a challenge for all satellite-based GNSS services because the flare directly interrupts a satellite’s feedback to the Earth.
Trimble continually optimizes the performance of our GNSS receivers and GNSS-based correction services. Multi-constellation, multi-frequency and sophisticated technology and algorithms help to mitigate these ionospheric impacts.
Trimble also provides several mitigation solutions within our current positioning portfolio, including our base stations, rover receivers and corrections services, including Trimble RTX® and Network-RTK software solutions. Trimble IonoGuard™ technology for civil construction, geospatial and OEM GNSS customers was designed to minimize GNSS signal interruptions.
To see recent availability and current atmospheric information, visit our GNSS Planning Online site to help you plan accordingly. Download our white paper below if you want to learn more about how IonoGuard works.
According to NASA, a solar flare incident may last from minutes to hours. Sometimes the same active region on the Sun can give rise to several flares in succession, erupting over the course of days or even weeks, though the impact may be able to be mitigated using technology. The longest known incident, known as the Great Quebec Blackout of 1989, lasted approximately 9 hours and affected approximately 6 million people, according to SpaceWeather.com.
Yes, you can expect impacts to vary from one geographic region to another geographic region, depending on the Earth’s rotation, tilt and general proximity to the Sun, on a given day or time.
Yes, these solar events occur on a continuing basis, the most severe events tend to occur on a 11-year cycle, approximately. This is highlighted in this chart below.
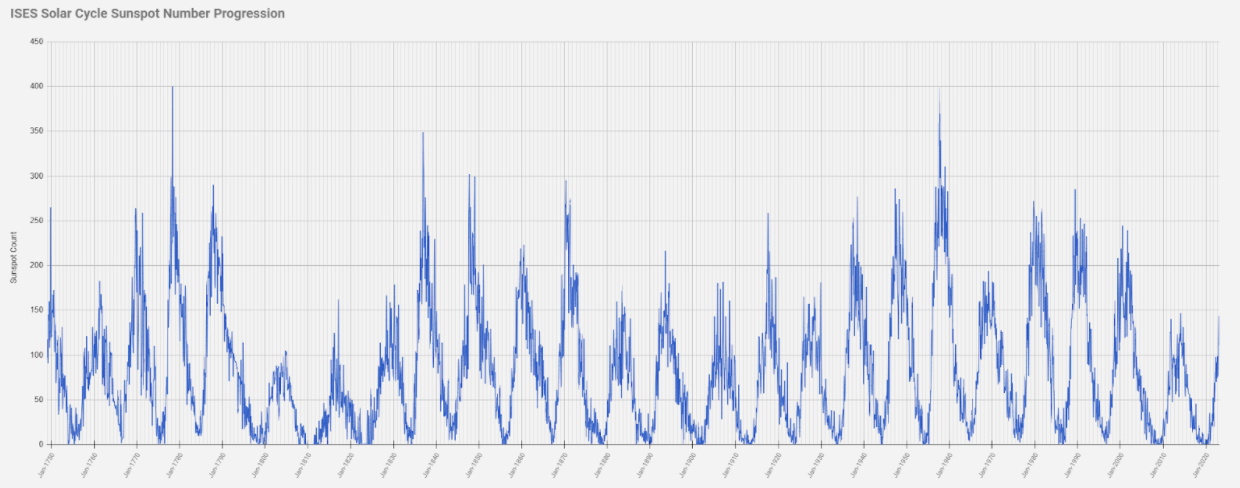
Source: NOAA National Weather Service Space Weather Prediction Center
We expect Solar Cycle 25 to peak 2024-2026.
Try Trimble RTX
RTK users may experience improved performance during an ionospheric event by using RTX technology. Test Trimble RTX performance with a free trial.
Learn more
These resources will provide you more detailed information about the sun’s activity and how and why solar flares impact satellite performance.
- NASA Blog: Solar Cycle 25
- NASA Solar Flare FAQs
- NOAA Solar Cycle Progression
- Wikipedia: Solar Cycle 25
- Trimble GNSS Planning Online - add your location information in the site’s “Settings” and view current atmospheric information by toggling the “TEC” and “Scintillation” buttons under “World View”.
